Throughout this article, we will analyze the most advanced studies on the prevalence of partial and total edentulism from the Universidad Mayor Real y Pontificia de San Francisco Xavier de Chuquisaca and oral cancer: genetics, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment conducted by the European University of Madrid.
What is Edentulism?
It is a condition where one or more teeth are missing. In other words, it refers to the loss of teeth, whether partial or total, distinguishing three types:
- Unitary: This is the most common, especially in the front part of the mouth.
- Partial: Several teeth are missing, but the patient still has some natural teeth.
- Total: The patient has no natural teeth.
What Are the Causes of Edentulism?
The main cause is poor or lack of oral hygiene, which leads to certain diseases such as:
Periodontitis
Gum disease, which starts with gingivitis and progresses to periodontitis if left untreated, causes damage to gum tissue. This causes the tooth to lose support and fall out.
Cavities
Due to the accumulation of bacteria from a lack of oral cleaning, they decay the tooth until they reach the root.
The tooth may break, falling out little by little or, in the worst case, the entire tooth may be lost.
Trauma
Although this is not related to dental hygiene, it is another cause of edentulism: A strong blow to the mouth can cause tooth avulsion, meaning the tooth is dislodged from its socket.
With proper care, there is a possibility that the tooth can be reimplanted. The same applies when it breaks: With appropriate care and reconstruction, it is possible to save the tooth.
What Does the Study Say?
This study was conducted in the town of Sucre-Chuquisaca, Bolivia. The choice of this location is due to the frequent oral health disorders among the population, resulting from a lack of oral health education, economic resources, and the high costs of dental care.
735 people between the ages of 15 and 85 were selected, of which 445 were women (60.5%) and 290 men (39.5%). They were divided into four age groups: 15-24, 25-39, 40-59, and 60-85 years respectively.
After the tests, it was found that 95.1%, equivalent to 669 individuals, suffered from edentulism, and only 4.9% did not. By gender, it was more predominant in females than in males.
In the younger age ranges, from 15 to 29 years, partial edentulism was detected, becoming more advanced as the age range increased.
Consequences of Edentulism
Since it is a loss of teeth, it can be solved with a minor intervention to insert teeth or prostheses into the spaces left.
Otherwise, it will have the following consequences for the mouth:
- Difficulty chewing, making it hard to eat various foods.
- Increased pressure on the remaining teeth in your mouth.
- Digestive problems due to not chewing food well and swallowing larger pieces.
- There will be foods you cannot eat.
- Aesthetic problems.
Oral Cancer: What Does the Study Say?
This malignant tumor affects any of the tissues of the oral cavity, including the lips, upper or lower jaw, tongue, cheeks, and throat.
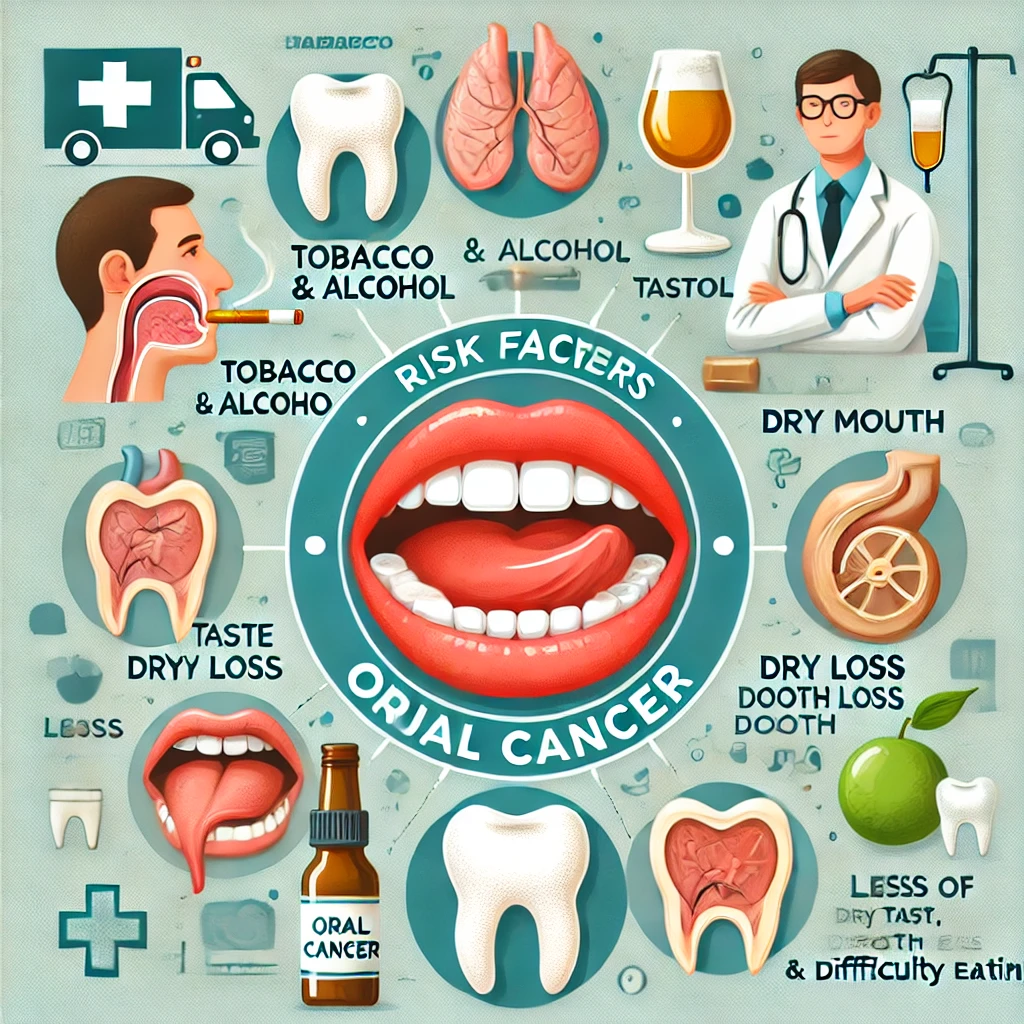
Risk Factors
According to the study, tobacco and alcohol are two of the most important factors, drastically increasing the risk if used together.
Particularly noteworthy are:
- Consumption of betel nut or areca nut.
- Chewing tobacco.
- Inverted smoking.
- Poorly fitting prostheses.
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Drugs such as diethylstilbestrol.
- Exposures to energies that cause direct damage to genes such as X-rays.
Consequences of Oral Cancer
Those who suffer from it, even after appropriate treatment, will experience the following effects:
- Loss or change in the sense of taste.
- Dry mouth.
- Tooth loss.
- Difficulty eating.
- Poor nutrition due to difficulty eating.
- Some people may need a feeding tube in the stomach after treatment.
- Weight loss.
- Difficulty speaking.
Is There a Way to Prevent Oral Cancer?
According to the study, three out of four oral cancers can be prevented by eliminating alcohol and tobacco consumption, which also reduces the risk of secondary tumors.
However, there is no guarantee that this can prevent the development of an oral tumor. And since it is so difficult to identify, especially in its early stages, it is best to avoid bad habits and, above all, practice good oral hygiene.
Remember, there are around 700 bacteria living inside our mouths, some good and some bad. Make sure to clean your mouth thoroughly after every meal, let the agents in toothpaste and mouthwash do their work, and reduce tobacco and alcohol consumption to a minimum.
Of course, do not forget to visit a specialist if you notice the first symptoms, to detect it in time and begin treatment.